Menu

Aesthetic Medicine includes all the medical procedures aiming to improve people’s physical appearance. Aesthetic is about enhancing someone’s features with no therapeutic and pharmacological action. There is little to no distinction between medicine and beauty when it comes to aesthetic medicine. Medicine and beauty are intricately intertwined when it comes to aesthetic medicine [1].
On what standards is based the “beauty assessment” before an aesthetic procedure whether its surgical or non-surgical? In reality, this evaluation could be considered as a conceptual assessment of the patient consulting an aesthetic doctor, as there is no existing consensus or guidelines. Most of the time, it is based on what the patient wants to be changed in order to improve the physical appearance [2]. The demand could be lips volumizing if the patient feels that his lips are too thin, the patient may ask his aesthetic doctor to manage his visible wrinkles, etc. The three strongest predictors for proceeding with treatment were patient’s prior treatment history, having a goal of rejuvenation for their procedures, and having an expectation for instant improvement after treatment [13].
Aesthetic procedures originated in the mid-1800s. It first started with external incisions in the facial region. In 1887, John Orlando Roe (1848–1915), an otolaryngologist from Rochester practiced the first intranasal corrective operation on the nose [3]. For a long time, aesthetic procedures used to be less practiced in residency programs but currently growing to be more and more practiced and becoming an important compound in the domain of plastic surgery with increasing in the number of interventions, revenues, staff and clinical research [4]. Aesthetic medicine then came along to offer a less invasive way to enhance the physical appearance [4].

Aesthetics includes surgical and non-surgical procedures. Concerning aesthetic surgery, the international Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS) published the results of its annual Global Survey on Aesthetic/Cosmetic Procedures. The results showed a 19.3% increase in procedures performed by plastic surgeons in 2021 with more than 12.8 million surgical procedures and 17.5 million non-surgical procedures performed worldwide. United Stated of America and Brazil are the countries with the highest demand for plastic surgery.
USA are leading the way with the most performed procedures worldwide (24.1% of the total) with 30.4% of all non-surgical procedures and 15.5% of all surgical procedures. Brazil and Japan are following USA with respectively 8.9% and 5.7% of total aesthetic procedures. It is also important to note that USA and Brazil are estimated to have the highest number of plastic surgeons, with more than 30% of the world's total plastic surgeons.
It’s important to know that aesthetic procedures should be practiced and qualified medical doctors with advanced knowledge of body and facial anatomy in order to ensure safe and efficient outcomes for the patient. Surgical procedures are referred to as “aesthetic surgery”. Aesthetic surgery is a branch of plastic surgery. It involves any surgical procedure that aim to improve the physical appearance of the patient [5]. Overall, Surgical procedures include Face lift, brow lift, eyelid surgery, rhinoplasty, labiaplasty, liposuction, breast augmentation, breast reduction, most of these procedures require local or general anesthesia [6]. But over time, aesthetic medicine is leaning towards less invasive techniques and away from formal surgeries [1]. Non-surgical procedures aim to optimize facial and body appearance in a less invasive way without having to undergo a surgery.
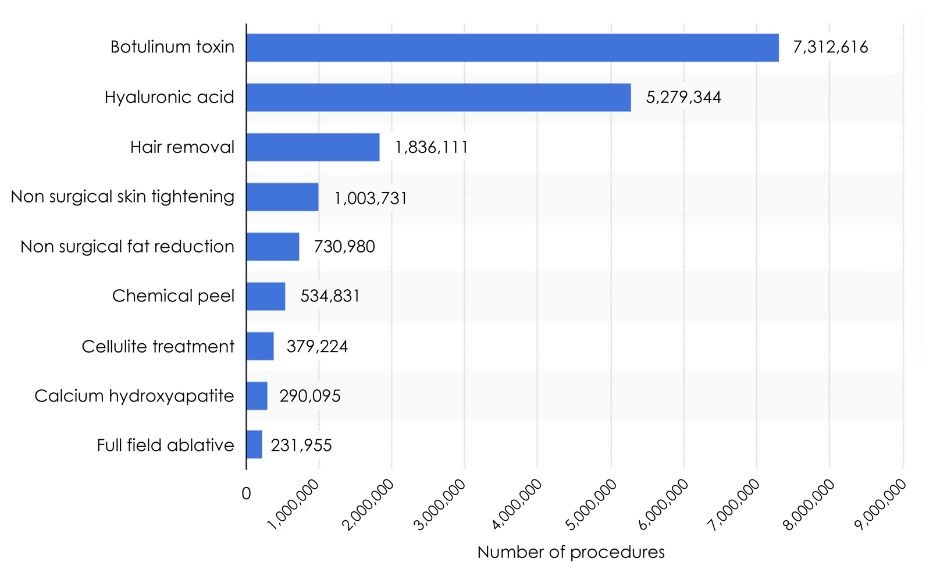
Examples of non-surgical less invasive procedures are skin surface procedures, dermal threads and injectables. Skin surface procedures include lasers, micro needling and chemical peeling. Laser is a high energy light pulse that target the skin layers and when it heals, the skin renovates itself. Micro needling is a procedure involving small needles rolled over the skin surface creating micro punctures that initiates inflammation and stimulate collagen production. And finally, chemical peeling is the creation of injury on skin by using chemical agents to stimulate new skin growth and improvement of appearance and texture. The top five non-surgical procedures are botulinum toxin, hyaluronic acid fillers, laser hair removal, skin tightening, and fat reduction.
Different types of products exists in the injectable category of products used for aesthetic purpose. The most used aesthetic injectable is botulinum toxin. This neurotoxin is injected to induce temporary muscle paralysis, therefore having effects on skin sagging issues of facial dynamic areas. Botox is mainly used to reduce glabellar frown lines, crow’s feet at the side of the eyes, forehead creases, wrinkles around the mouth, nasolabial folds and smoothing out neck and chest/cleavage wrinkles. However, Botox only targets muscle-controlled wrinkles and fine lines and not the ones caused by photodamage or volume deficiency. Therefore it’s important to have alternative techniques to improve volume deficiency and photodamage induced wrinkles and fine lines [7]. Dermal fillers are an option for treatment of volume deficiency, scars and skin aging signs such as wrinkles, folds and fine lines etc. Examples of fillers are Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA), Poly-L-lactic Acid, Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), deoxycholic acid fillers and Hyaluronic Acid (HA) [9]. Hyaluronic acid is the most used dermal filler for aesthetic purpose. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a disaccharide composed polymer (N-acetylglucosamine and D-glucuronic acid). It’s the most abundant glycosaminoglycan in the skin but its amount decreases with age [16]. With age, human skin is losing hyaluronic acid and it appeared pertinent to compensate hyaluronic acid loss thanks to hyaluronic injection. HA fillers are mostly used for volume defects and for skin quality improvement. Skin quality enhancement with hyaluronic acid is often made by mesotherapy techniques. Mesotherapy is basically defined by multiple points intra-dermal injections of a mixture of compounds thanks to fine needles. The aim of this technique is mainly to enhance the skin quality [10]. Injectable biodegradable HA fillers are categorized as class III medical devices by European Regulations. Providing different types of HA fillers and application techniques is relevant to adapt to skin needs, the zone to treat and the targeted outcomes. Their differences can lay in their structural and physico-chemical characteristics, such as the HA particle size, amount of free HA present, HA concentration, degree and cross-linking methods, HA chain sizes etc. [9].
Whether they are surgical or non-surgical, aesthetic procedures aim to enhance the appearance which may bring many advantages to the patient. Especially when it comes to self-appreciation of appearance by people after undergoing aesthetic treatments. Indeed, Aesthetic Medicine not only enhances the physical appearance of the patient, but may also improve self-esteem and confidence. Self-esteem is important when it comes to social interactions whether on the personal level or the professional level. In the current society, body and face image can be crucial. Beauty campaigns and medias are involved in showing the new desired standards for the "perfect face and body" appearance. In the era of internet and social media, Aesthetic Medicine is more and more under the spotlights as an opportunity to quickly fix people's complexes, therefore improve their psychological state and fulfil the societal expectations of what beauty should look like.
[1] Atiyeh BS, Rubeiz MT, Hayek SN. Aesthetic/Cosmetic Surgery and Ethical Challenges. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020 Aug;44(4):1364-1374.
[2] Choi J. Cosmetic Surgery: Is It Science or Art? Arch Plast Surg. 2015 Sep;42(5):672-4.
[3] Rogers BO. The development of aesthetic plastic surgery: A history. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1976 Dec;1(1):3-24. [4] Perdikis G, Eaves FF, Glassman GE, Walker S, Huang LC, Mast B, Damitz L, Rubin JP, Serletti JM, Hansen J, Potochny J, Kenkel J, Taub PJ, Sobczyk S, Gilman RH, Saint-Cyr MH, Cederna P. Aesthetic Surgery in Plastic Surgery Academia. Aesthet Surg J. 2021 Jun 14;41(7):829-841.
[5] https://www.isaps.org/discover/about-isaps/global-statistics/reports-and-press-releases/global-survey-2021-full-report-and-press-releases/
[6] De Souza MM, Jewell AD, Grief SN, Vail BA. Plastic Surgery for Women. Prim Care. 2018 Dec;45(4):705-717.
[7] Devgan L, Singh P, Durairaj K. Minimally Invasive Facial Cosmetic Procedures. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;52(3):443-459.
[8] Dayan S, Rivkin A, Sykes JM, Teller CF, Weinkle SH, Shumate GT, Gallagher CJ. Aesthetic Treatment Positively Impacts Social Perception: Analysis of Subjects From the HARMONY Study. Aesthet Surg J. 2019 Nov 13;39(12):1380-1389.
[9] Ballin AC, Brandt FS, Cazzaniga A. Dermal fillers: an update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015 Aug;16(4):271-283.
[10] Sivagnanam G. Mesotherapy - The french connection. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2010 Jan;1(1):4-8. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.64529. PMID: 21808584; PMCID: PMC3142757.
[11] Rogers, B.O. John Orlando Roe—Not Jacques Joseph—The father of Aesthetic Rhinoplasty. Aesth. Plast. Surg. 10, 63–88 (1986).
[12] ISAPS - global-statistics - global-survey-2021-full-report
[13] Sylvia P B Ramirez, Gunther Scherz & Helen Smith (2021) Characteristics of Patients Seeking and Proceeding with Non-Surgical Facial Aesthetic Procedures, Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 14:, 197-207
[14]https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/aesthetic-medicine-market
[15] Kaplan JB. Aesthetic self-esteem. Plastic Surgical Nursing : Official Journal of the American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgical Nurses. 2015 Jan-Mar;35(1):33-39
[16] Valachová K, Šoltés L. Hyaluronan as a Prominent Biomolecule with Numerous Applications in Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 30;22(13):7077.
 What could be considered a healthy skin?
What could be considered a healthy skin?
check_circle
check_circle