Menu

Carnosine is a small dipeptide well-document in the Scientific Literature for its antioxidant properties. Carnosine is one of the so-called “anti-ageing molecules” and Carnosine is widely used in the Cosmetic field to defy ageing skin signs and to improve skin texture and skin quality.
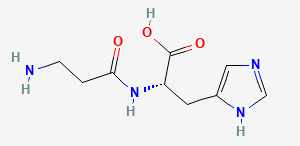
Carnosine is a small endogenous water soluble dipeptide composed of two amino acids, alanyl and histidine. This molecule is naturally present in vertebrates organisms especially in cardiac and skeletal muscles, nervous tissues, brain.
Carnosine has been discovered in 1902 by the biochemist Vladimir Gulevich and his research team at the Charkow University [14, 15].
Many studies have identified different biological properties of Carnosine, among which the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiglycation activities with targets in numerous mechanisms related to skin ageing [2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 13, 14] .

Skin ageing is a succession of physiological changes that the skin undergoes over time. This complex process is doomed to happen with age but multiple external factors that promote a premature skin ageing [8, 11]. Since skin is the first physical barrier against external threats, protecting it from accelerated ageing appears to be important in order to defy skin ageing [4, 8, 11]. Some biomolecules have been shown to have effects on skin ageing signs, therefore such molecules started being used in many skin care products. This article will focus on one of these molecules: Carnosine.
Exposome is a description of total exposure of both external and internal factors during the lifetime. as well as the response of the human body to these factors that lead to biological and clinical signs of skin ageing. Internal factors include intrinsic ageing process and the changes that go with it. External factors are the combination of all the environmental threats to which the skin is exposed such as UV rays, pollution, temperature, smoking, lack of sleep, bad nutrition and stress. Poor Lifestyle can affect the skin quality and accelerate the skin ageing signs [11].
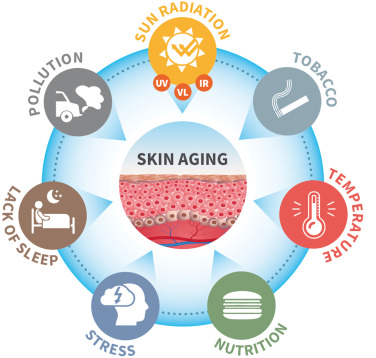
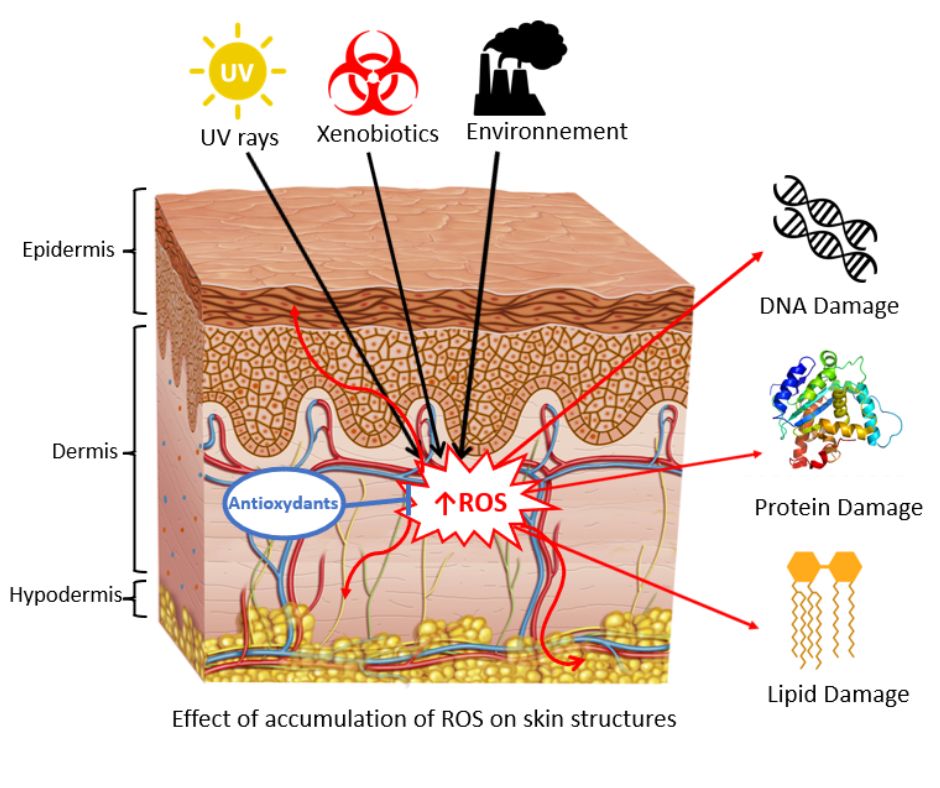
They might affect the skin cells causing premature skin ageing. Skin ageing signs are mainly caused by increasing of oxidative stress within time. Oxidative stress is known to induce skin damage. Adding to that, exposure to external factors increases even more the oxidative stress leading to a higher production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) that promotes damage on skin tissue (fatty acids, proteins, DNA). Oxidative stress is an imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants in favor of the oxidants, leading to a disruption of redox signaling and control and/or molecular damage. Oxidative stress can occur when the production of Reactive oxygen species is too much to handle for the natural antioxidant agents in the tissue. Antioxidants are molecules that can neutralize Reactive oxygen species
Carnosine is widely used molecules in so-called anti-ageing cosmetic products. Many studies have shown the effect of carnosine to protect against skin ageing visible signs [3]. Scientific Literature has reported anti-ageing effects of Carnosine thanks to its antioxidant activity [6]. Carnosine antioxidant effects are related to its ability to scavenge ROS such as free radical molecules in order to neutralize their oxidative effects on the skin tissue [3, 5].
On a molecular level, carnosine could prevent the alteration of cellular systems and pathways such as proteins alteration i.e. (glycation), altered calcium signaling, disruption of the mitochondrial functions and Enzymes expression, fatty acid peroxidation, DNA damage. By defying the skin ageing process, carnosine might have an impact on skin quality maintaining [3, 4, 5].
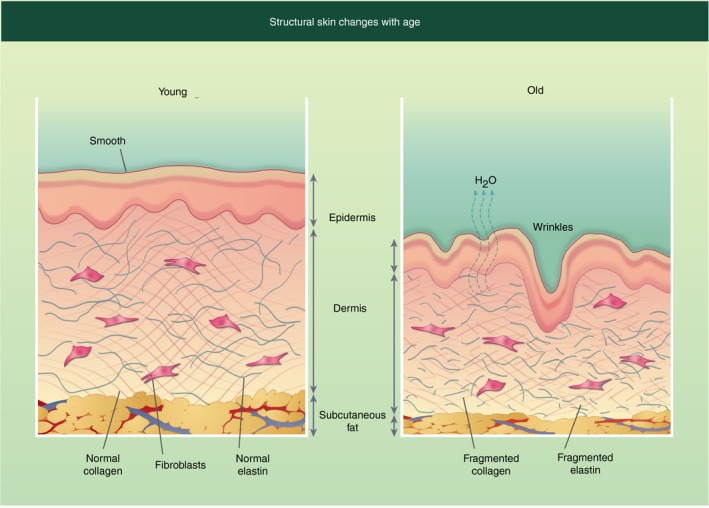
Furthermore, Carnosine has been reported in the Literature to help protecting skin tissue and its proteins from abnormal modifications induced by oxidative stress. One of those modifications is protein glycation known for impairing proteins functions. Impairment of the proteins functions leads to the loss of skin elasticity, firmness and skin tissue integrity etc. For example, glycations occurring in collagen fibers can rigidify collagen fibers until they eventually break them down which may contribute to the creation of wrinkles in the skin [7, 8].
Overall, carnosine may be a relevant molecule involved in protective processes of the skin compartments against oxidative stress during skin ageing. Numerous Studies have reported that products containing Carnosine improve facial skin characteristics with a significant decrease in sagging skin and wrinkles, a significant increase in skin hydration, firmness, elasticity and an improved skin texture [8].
[1] Lintner, K.; Peschard, O. Biologically active peptides: From a laboratory bench curiosity to a functional skin care product. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2000, 22, 207–218
[2] Cararo JH, Streck EL, Schuck PF, Ferreira Gda C. Carnosine and Related Peptides: Therapeutic Potential in Age-Related Disorders. Ageing Dis. 2015 Oct 1;6(5):369-79.
[3] Aiello G, Rescigno F, Meloni M, Baron G, Aldini G, Carini M, D'Amato A. Oxidative Stress Modulation by Carnosine in Scaffold Free Human Dermis Spheroids Model: A Proteomic Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 27;23(3):1468.
[4] Radrezza S, Carini M, Baron G, Aldini G, Negre-Salvayre A, D'Amato A. Study of Carnosine's effect on nude mice skin to prevent UV-A damage. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Sep;173:97-103.
[5] Boldyrev AA, Aldini G, Derave W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol Rev. 2013 Oct;93(4):1803-45.
[6] Hipkiss AR, Brownson C, Bertani MF, Ruiz E, Ferro A. Reaction of carnosine with aged proteins: another protective process? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Apr;959:285-94.
[7] Babizhayev MA, Deyev AI, Savel'yeva EL, Lankin VZ, Yegorov YE. Skin beautification with oral non-hydrolized versions of carnosine and carcinine: Effective therapeutic management and cosmetic skincare solutions against oxidative glycation and free-radical production as a causal mechanism of diabetic complications and skin ageing. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012 Oct;23(5):345-84.
[8] Narda M, Peno-Mazzarino L, Krutmann J, Trullas C, Granger C. Novel Facial Cream Containing Carnosine Inhibits Formation of Advanced Glycation End-Products in Human Skin. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2018;31(6):324-331.
[9] Lorigo, Margarida & Cairrao, Elisa. (2019). Antioxidants as stabilizers of UV filters: an example for the UV-B filter octylmethoxycinnamate. Biomedical Dermatology. 3. 11. 10.1186/s41702-019-0048-9.
[10] National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 439224, Carnosine. Retrieved September 18, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Carnosine.
[11] Krutmann J, Bouloc A, Sore G, Bernard BA, Passeron T. The skin ageing exposome. J Dermatol Sci. 2017 Mar;85(3):152-161.
[12] Chambers ES, Vukmanovic-Stejic M: Skin barrier immunity and ageing. Immunology. 2020, 160:116-25. 10.1111/imm.13152
[13]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vladimir_Gulevich
[14] Caruso G, Di Pietro L, Cardaci V, Maugeri S, Caraci F. The therapeutic potential of carnosine: Focus on cellular and molecular mechanisms. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2023 Mar 7;4:100153.
[15] Wl. Gulewitsch; S. Amiradžibi (1900). Ueber das Carnosin, eine neue organische Base des Fleischextractes. , 33(2), 1902–1903
[16] Rinnerthaler M, Bischof J, Streubel MK, Trost A, Richter K. Oxidative stress in aging human skin. Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 21;5(2):545-89.
check_circle
check_circle
Medical Devices products are intended for use by Medical Doctors only, with experience in the anatomy and physiology of the injection site.
Revitacare requires your attention on the fact that none of the information contained in this website should be considered a solicitation, or advertisement for any medical procedure or health product in general.